|


We should not be surprised at
Rockefeller's hand in this as John D. Rockerfeller' father made his fortune
selling "patent" medicine.
William Avery "Bill" Rockefeller, Sr.
(November 13, 1810 – May 11, 1906) was
an American confidence man
who went by the alias of Dr. William Levingston.
He worked as
a traveling "botanic physician" who
sold elixirs.
His sons, John Davison Rockefeller (July 8,
1839 – May 23, 1937) and William
Avery Rockefeller, Jr. (May 31, 1841 – June 24, 1922), were
Standard Oil
co-founders.
Several systems for
induction of transgene expression in
plants exist.
Initially inducible systems are used in tobacco,
rice, tomato and
corn.
Inducible systems offer the possibility of deregulating gene expression
levels at particular stages of plant development and in particular tissues of
interest.
The more precise temporal and spatial control, obtained by
providing the transgenic plant with the appropriate chemical compound or
treatment, permits analysis of the function of those genes required for plant
viability.
Specific mutation of a gene can be achieved by a two-step
process.
Introduction of loxP sites around a functionally essential
genomic part followed by a cell type-specific Cre recombinase-mediated excision
of the loxP flanked sequence.
The same strategy can be used for cell
type-specific overexpression of a transgene, when a strong overall expressing
promoter is separated from the coding region of a gene of interest by loxP
flanked 'STOP' sequences.
In both scenarios, a Cre recombinase
transgene provides spatial control.
Once Cre expression
has been switched on and recombination has occurred, the resultant change in
gene expression is, in most cases, irreversible.

"Being
an educated person
requires - being a full
person, requires a certain ability to
deal with dissonance.
You know, I'm Jewish, was
raised Jewish.
I brought up my kids in the Jewish
tradition.
We celebrate Jewish
traditions.
At the same time,
I'm a scientist.
And data means an awful lot to me.
I clearly believe in
evolution and it's really hard to get away from the
undirected nature of change.
The
science leaves very little room for
purpose in evolution." - Eric Lander
1902
Archibald Garrod described the inherited disorder alkaptonuria as an inborn
error of metabolism.
He proposed that a gene mutation causes a specific
defect in the biochemical pathway for eliminating liquid wastes.
The phenotype of the disease -
dark urine - is a reflection of
this error.
1910 The term "pleiotropie" is first
coined by Ludwig Plate in Festschrift.
He defined pleiotropy as
occurring when "several characteristics are dependent upon ... [inheritance];
these characteristics will then
always appear together and may thus appear correlated".
1930 Ronald Fisher in Geometric Model implies locus
mutations as being capable of affecting
essentially all traits.
1941 Inborn error of
metabolism is rigorously proven by George Beadle and Edward Tatum using the
simple bread mold Neurospora.
Molds exposed to radiation lose the ability to
produce essential
nutrients, and this slowed, even stopped the growth of the mold.
Growth could be restored providing mutated mold a specific nutrient.
Hypothesis: mutations inactivate enzyme (protein) needed to absorb
nutrients.
If a cell stitches exons together in one way, it makes one
protein.
Stitching the exons together in another way, it makes a
different protein.
Cells making
antigens may mistranslate
proteins and creat autoantigens.
95%
of the genes in the human genome participate in this process.
Alternative pre-mRNA splicing in neurons
Rbfox proteins regulate splicing of a large multiprotein
complex
Relationship between Alternative Splicing and Proteomic
Complexity
Splicing
regulator PTBP1 controls the activity of the transcription factor Pbx1 during
neuronal differentiation


Molecular genetics is primarily concerned with the
inter-relationship
between information macromolecules DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
and RNA (ribonucleic acid) and
how molecules are used to
synthesize polypeptides.
As the vast majority of gene expression is
dedicated to polypeptide synthesis,
proteins are the major functional end-points of the DNA template and account
for the majority of the dry weight of a cell.
The term
protein is derived from the
Greek proteios, meaning 'of the first rank' and reflects the important roles of
proteins in diverse cellular functions as enzymes, receptors, storage proteins,
transport proteins (tRNA), transcription
factors, signaling molecules, hormones, etc.
Proteins are composed of
polypeptide molecules
which may be modified by the addition of various
carbohydrate side chains
or other chemical groups.
Like DNA and RNA,
polypeptide molecules are
polymers consisting of a linear sequence of repeating units, in this case
amino acids.
The
latter consist of a positively charged amino group and a negatively charged
carboxylic acid (carboxyl) group connected by a central carbon
atom to which is attached an identifying
side chain.
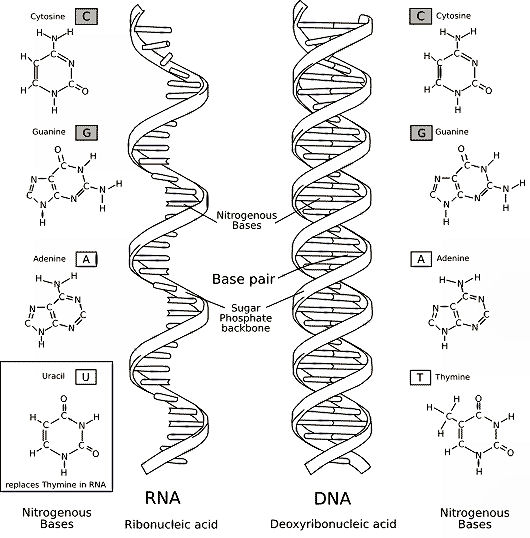
Charged molecules are highly soluble in water.
Both DNA
and RNA are negatively charged (polyanions) because of the
organophosphate
charges present in their component nucleotides.
Depending on their
amino acid composition, proteins
may carry a net positive charge
(basic proteins) or a net negative charge (acidic proteins).
The
hydrogen bonding potential
of water molecules means that molecules with polar groups (including DNA,
RNA and proteins) can form multiple interactions with the
water molecules, leading to their
solubilization.
Thus, even electrically neutral proteins are often
readily soluble if they contain an appreciable number of charged or neutral
polar amino acids.
The
linear backbone of a DNA
molecule and of an RNA molecule consists of
alternating sugar residues and organophosphate groups.
Whereas
the RNA molecules within a cell normally exist as single molecules, the
structure of DNA is a double helix in which two
DNA molecules (DNA
strands) are held together by
weak hydrogen bonds
to form a DNA duplex.
DNA can adopt different types of helical
structure.
Genetic information is encoded by the linear sequence of
bases in the DNA strands (the primary structure).
Intermolecular
hydrogen bonding permits RNA-DNA duplexes and double-stranded RNA formation
which are important requirements for gene expression.
Hydrogen bonding can occur between bases
within a single DNA or RNA molecule.

The expression of genetic
information in all cells is mostly a one-way system: DNA specifies the
synthesis of RNA and RNA specifies the synthesis of polypeptides, which
subsequently form proteins.
Because of its universality, the DNA >
RNA > polypeptide (protein) flow of genetic information has been described
as the central dogma of gene expression molecular biology.
The shape and
structure of proteins is a crucial aspect of molecular gene expression and
links our understanding of gene expression to the biology of the cell.
While primarily concerned with protein molecules that act on DNA and
RNA sequences, such as transcription factors and histones, the study of gene
expression also focuses on where in the cell expression is modulated.
In
fact, the modulation of gene expression can occur in the nucleus, the
cytoplasm, or even at the cell membrane due to the impact of proteins on RNA in
those cellular subregions.
In his Nobel lecture, given shortly after he
joined the Rockefeller Institute
for Medical Research, Edward L. Tatum
outlined the concepts
fundamental to his one-gene, one-enzyme (understood today as one-gene,
one-polypeptide) hypothesis:
all biochemical
processes in all organisms are under genetic control;
biochemical
processes are resolvable into a series of individual reactions;
each
reaction is controlled in a primary fashion by a single gene - 1:1
correspondence of gene and biochemical reaction exists;
mutation of a
single gene results only in an alteration in the ability of the cell to carry
out a single primary chemical reaction.
Geneticist George W. Beadle and
the biochemist Edward L. Tatum were awarded the Nobel Prize largely through the
auspices of the Rockefeller Foundation, for
this hypothesis which turned out to be
entirely false !!!
A cell uses the DNA molecule in the nucleus as
a template for protein
production.
The cell sends a 'messenger RNA' =
mRNA into the nucleus to retrieve the encoding.
The mRNA takes the
copied "recipe" out of the nucleus to the ribosome, which is where proteins are
made.
In eukaryotic cells (the kinds of cells
found in plants and animals), however,
something very interesting
happens before the mRNA leaves the nucleus.
Some parts of the mRNA
are cut away, and the remaining parts are then stitched back
together.
The parts of the mRNA that are cut away never leave the
nucleus, so they are called introns (they stay IN the nucleus).
Introns
regulate the amount of the various proteins that are being made.
"For a
while, geneticists didn't know the purpose of introns, so in typical
evolutionary fashion, many decided that they had no purpose, and introns were
lumped into the category of "junk DNA." As
we have learned more about
genetics, we have learned that the evolution-inspired idea of "junk DNA" is,
itself, junk, although some evolutionists still cling to it." - Jay L.
Wile
The remaining parts that are stitched together are called exons
(they EXit the nucleus).
Each exon represents a "module" of useful
information.
If the cell stitches the exons together in one way, it
makes one protein.
If it stitches the exons together in another way, it
makes a different protein.
As a result, a single gene can actually produce
many different proteins.
ALL of
molecular biology is based on this
fatal error.
Genetically modified organisms and the industrial
manipulation of molecular genetics is based on a theory that has turned out to
be entirely false.
Unintended toxic proteins is the
transgenic standard !

mRNA vaccine delivery using lipid
nanoparticles
The promise of activating the humoral and the
cellular arms of the immune
system has driven the development of DNA
vaccines over the last decades.
Live-attenuated vaccines are the most potent in
activating both cellular and humoral immunity.
However, these vaccines
exhibit considerable safety drawbacks.
Attenuated pathogens have the potential to revert to
a pathogenic form.
DNA therapeutics have to reach the nucleus, while
for mRNA therapeutics, the cytosol is the target.
DNA and mRNA vaccines
share many similarities.
The main difference between the two approaches
is the target location for the delivery of the oligonucleotides.
mRNA
vaccines have generated significant interest to replace traditional vaccines
due to a number of important attributes that they possess.
mRNA vaccines
elicit a potent immune response
including antibodies and cytotoxic
T-cells.
Successful cytosolic delivery of mRNA, encoding for an
antigen, results in vaccine epitope synthesis of the transfected cells.
As a result, mRNA therapeutics are easier to deliver as they do not
have to cross the nuclear membrane.
mRNA synthesis and purification are
fast, easy and low cost in comparision, even though mRNA is highly unstable
under physiological conditions.
Several strategies have been developed
for RNA delivery, including RNA conjugates, modified RNA, viral vectors,
microparticles and nanoparticles.
Viral vectors are the obvious choice
for delivery, as virus have naturally evolved to become highly efficient at
nucleic-acid delivery.
Lipid nanoparticles
(LNPs) are among the most frequently used vectors for in vivo RNA
delivery.
In addition to ionizable cationic lipids, phospholipids,
cholesterol and lipid anchored polyethylene glycol (PEG) are the most commonly
used components for LNP formulations.
Lipids are
fatty acids insoluble in
water but soluble in organic
solvents.
Lipids come in four forms natural oils/fats, waxes,
phospholipids and steroids.
The theory of vesicle formation assumes that LNP formation is based on
disk-like bilayered fragments whose edges are stabilized by ethanol.
Phospholipids play a structural role in LNPs helping with
the formation and disruption of
the lipid bilayer to facilitate endosomal escape.
Furthermore, some
phospholipids possess polymorphic features and promote a transition from a
lamellar to a hexagonal phase in the endosome.
The properties of
individual LNPs strongly depend on local, microscopic mixing rates; diffusive
transport effects can lead to LNPs with variable compositions.
Early synthesis methods
relied on the formation of micrometer-sized vesicles by suspending lipids in
water, followed by sonication to produce submicrometer sized particles.
This top–down approach has many limitations, including molecular
degradation, contamination and lack of scalability.
Extrusion of a
lipid film through a small filter has been
a popular synthesis method, often used at the laboratory scale using syringe
miniextruders.
Other synthesis methods include the condensation of a
lipid ethanol solution by rapid injection into a vigorously stirred aqueous
buffer.
Newer synthesis methods directly mix the lipid–ethanol
phase with an aqueous solution of mRNA in a small T-piece; flow, mixing rates,
controlled by pumps.
In this way, LNPs with diameters of 70 nm or
larger and high encapsulation efficiencies can be generated.
Decorating
the LNPs with immune cell receptors may facilitate the uptake by the desired
type of immune cells.
The most important
targets for mRNA vaccines are antigen presenting cells (APCs), with dendritic
cells (DCs) likely being the most relevant cell type.
APCs are
concentrated at high density in lymph
nodes (LNs).
The theory is transfected DCs express the mRNA-encoded
antigen.
The antigens are subsequently processed by the proteasome, and
the generated peptide epitopes enter the endoplasmic reticulum where they are
loaded onto major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecules.
The MHC class I molecules are transported to the surface of the cell
where the epitopes are presented to CD8 T cells along with costimulatory
signals.
Resence of antigen fragments on MHC II induces antigen-specific
antibodies.
There
is a pathway for the presentation of protein antigens on MHCI, not yet fully
understood, often too weak to elicit a potent
cytotoxic immune response.
Aluminum salts, used to enhance the
immune response of
traditional vaccines, thought to be related to the effect of prolonged
antigen exposure, is still not understood in detail.
Including adjuvants
with the LNPs provides a way to further increase the potency of the vaccine and
guide the immune
response in the desired direction.
In order to mount a strong
adaptive immune response, a vaccine needs to reach the LNs, where
T lymphocyte activation and
proliferation occurs.
Affinity maturation and isotype switching of
antibodies takes place in germinal centers in the LNs.
Intradermal (ID)
injection delivers LNPs directly into the skin, an organ which is densely
populated with Langerhans cells in the epidermis and with multiple DC subtypes
in the dermis.
The ID route of administration has been shown to
effectively induce a Th1 type immune response and cytotoxic T lymphocyte induction for
mRNA–LNP vaccines.
IV injections of LNP–mRNA vaccines are less
common because of the potential of systemic side effects.
Injecting
immunogenic material in the blood stream may lead to
massive cytokine production,
a cytokine storm,
that can lead to shock and
death.
The thickness of
polyethylene
glycol (PEG) coating on the LNPs is critical.
Coating the particles
with a lipid-anchored PEG containing lipid can reduce complement
activation.
PEG coating strongly influences the properties of the LNPs
and has to be tailored carefully.
A higher PEG content usually
increases the blood circulation time of LNPs, while reducing cellular uptake
and interaction with the endosomal membrane.
The surface of an LNP may
be decorated with specific targeting sequences which help with homing and
subsequent uptake.
Self-amplifying mRNA has been used to prolong protein
expression and to increase the immunogenicity of mRNA vaccines, which leads to
a dramatic decrease in the effective dose compared with nonreplicating
mRNA.
Self-amplifying mRNAs, also termed
replicons, are based on retrovirus where the structural viral proteins are replaced with
suitable mRNA encoding antigens, as well as with
RNA polymerases for
RNA replication.
The most studied replicons are derived from alphavirus
and flavivirus.
When introduced into the cytosol of cells, the mRNA
will express the heterologous genes and replicate.
Through mRNA
amplification, large
amounts of desired antigens can be synthesized, accounting for up to 20% of
total cell protein.
Optimization of Lipid Nanoparticles for Intramuscular
Administration of mRNA Vaccines
Infection of cells by coronavirus is effected through the
spike glycoprotein.
The coronavirus
that causes severe acute respiratory syndrome infects cells expressing the
receptor angiotensin-converting enzyme 2.
Here we show that codon
optimization of the SARS-CoV spike glycoprotein gene substantially enhanced
spike protein expression.
Two retrovirus,
simian immunodeficiency virus and murine
leukaemia virus, both expressing green fluorescent
protein and pseudotyped with SARS-CoV spike glycoprotein variants, infected
HEK293T cells stably expressing ACE2.
Infection mediated by an spike glycoprotein variant
whose cytoplasmic domain had been
truncated and
altered to include a fragment of the cytoplasmic tail of the
human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope
glycoprotein was substantially more efficient than that mediated by
wild-type spike glycoprotein.
SARS-CoV-2 variants, spike mutations and immune
escape
SARS-CoV is not closely related to any of the
three previously defined genetic and
serological coronavirus groups, although it may be distantly related to
group 2 coronavirus.
SARS-CoV spike glycoprotein,
a surface glycoprotein
facilitating coronavirus entry into receptor-bearing cells, is distinct from
other coronavirus.
The gene encoding the spike glycoprotein of SARS-CoV
contains many codons used infrequently in mammalian genes for efficiently
expressed proteins.
We generated a codon-optimized form of the spike
glycoprotein gene and compared its expression with the spike glycoprotein gene
of the native viral sequence.
spike glycoprotein was readily detected
in HEK293T cells transfected with a plasmid encoding the codon-optimized spike
protein.
No spike glycoprotein was detected in cells transfected with a
plasmid encoding the native spike glycoprotein gene.
When transfected
cells were infected with recombinant vaccinia
virus expressing T7 polymerase, which can transcribe message in the
cytoplasm, spike glycoprotein was efficiently produced from plasmids containing
either codon-optimized or native genes.
The codon-optimized gene
expressed more than twice as much spike glycoprotein as the native viral
sequence.
Spike glycoprotein can be efficiently expressed from the
codon-optimized plasmid without T7 polymerase, we used this plasmid in
subsequent studies.

In the quest for the development of pharmacological
switches that control gene expression, no system has been reported that
regulates at the translational level but several systems have been
constructed:
-Tetracycline-inducible transgenic systems [tetracycline
transactivator (tTA) or 'Tet-Off' and reverse tetracycline transactivator
(rtTA) or 'Tet-On'] allow for reversible temporal regulation of transgene
expression .
Between these, rtTA is better suited for rapid induction
of gene expression.
-To permit small-molecule control of transgene
translation a farnesyl transferase inhibitor-responsive translation initiation
factor was constructed.
This
artificial protein
is a three-component chimaera consisting of the ribosome recruitment core of
the eIF4G1 eukaryotic translation initiation factor, the RNA-binding domain of
the R17 bacteriophage coat protein and
the plasma membrane localization CAAX motif of farnesylated H-Ras.
This
membrane-delocalized translation factor is inactive unless liberated in the
cytosol.
Farnesyl transferase inhibitor FTI-277 prevents the membrane
association of the CAAX motif and thus increases the cytoplasmic levels of the
eIF4G fusion protein, which is then capable of inducing translation of the
second cistron of a bicistronic messenger RNA containing an R17-binding site in
its intercistronic space.
- The concept of cisgenesis could become a
promising approach in future apple breeding.
However, cisgenesis
depends on the availability of effective tools for the
production of marker-free
genetically modified plants.
The development of such plants was recently
shown to be possible using a heat shock
inducible Flp/FRT recombinase based transformation system allowing the
excision of the marker gene from the genome of genetically modified apple plant
tissue.
- A new laser mediated
method heat shocks
groups of cells allowing precise spatio-temporal control of gene expression
without requiring knowledge of specific enhancer sequences.
-The
baculovirus Autographa californica nucleopolyhedrovirus (AcNPV) has been widely
used to achieve a high level of foreign gene expression in insect cells, as
well as for efficient gene transduction into mammalian cells without any
replication.
In addition to permitting efficient gene
delivery, baculovirus has been shown to induce host innate immune responses in
various mammalian cells and in mice.

The major barrier to the clinical application of adenovirus
gene therapy
for diseases that require stable transgene expression is the immunogenicity of
recombinant adenovirus, which ordinarily limits the duration of its effects to
a period of about 2 weeks.
If
tolerance to
adenovirus could be induced then transgene expression could be prolonged if
T lymphocytes underwent
thymic selection in the presence of adenovirus antigens.
The ability to
achieve unresponsiveness to a recombinant adenovirus after inoculation of the
thymus in neonates extends the
paradigm of intrathymic tolerance induction.
T lymphocytes are
exquisitely poised to respond rapidly to
pathogens and have proved an instructive model for
exploring the regulation of inducible genes.
Individual genes respond
to antigenic stimulation in different ways, and it has become clear that the
interplay between transcription factors and the chromatin platform of
individual genes governs these
responses.
Understanding of the
complexity of the chromatin platform and the
epigenetic
mechanisms that contribute to transcriptional control has expanded
dramatically in recent years.
These mechanisms include the
presence/absence of histone modification marks, which form an epigenetic
signature to mark active or inactive genes.
These signatures are
dynamically added or removed by epigenetic enzymes, comprising an array of
histone-modifying enzymes, including the more recently recognized
chromatin-associated signalling kinases.
In addition,
chromatin-remodelling complexes physically alter the chromatin structure to
regulate chromatin accessibility to transcriptional regulatory factors.
The advent of genome-wide technologies has enabled characterization of
the chromatin landscape of T lymphocytes
in terms of histone occupancy, histone modification patterns and transcription
factor association with specific genomic regulatory regions, generating an
image of the T lymphocyte epigenome.
 |
|
 |
This web site is not a commercial web site and
is presented for educational purposes only.

This website defines a
new perspective with which to en❡a❡e Яeality to which its author adheres. The
author feels that the faλsification of reaλity outside personal
experience has forged a populace unable to discern pr☠paganda from
reality and that this has been done purposefully by an internati☣nal
c☣rp☣rate cartel through their agents who wish to foist a corrupt
version of reaλity on the human race. Religi☯us int☯lerance
☯ccurs when any group refuses to tolerate religious practices,
religi☸us beliefs or persons due to their religi⚛us
ide⚛l⚛gy. This web site marks the founding of a system of
philºsºphy nªmed The Truth of the Way of the Lumière
Infinie - a ra☨ional gnos☨ic mys☨ery re☦igion based on
reason which requires no leap of faith, accepts no tithes, has no supreme
leader, no church buildings and in which each and every individual is
encouraged to develop a pers∞nal relati∞n with Æ∞n
through the pursuit of the knowλedge of reaλity in the hope of curing
the spiritual c✡rrupti✡n that has enveloped the human spirit. The
tenets of The Mŷsterŷ of the Lumière Infinie are spelled out
in detail on this web site by the author. Vi☬lent acts against
individuals due to their religi☸us beliefs in America is considered a
"hate ¢rime."
This web site in no way c☬nd☬nes
vi☬lence. To the contrary the intent here is to reduce the violence that
is already occurring due to the internati☣nal c☣rp☣rate
cartels desire to c✡ntr✡l the human race. The internati☣nal
c☣rp☣rate cartel already controls the w☸rld
ec☸n☸mic system, c☸rp☸rate media w☸rldwide, the
global indus✈rial mili✈ary en✈er✈ainmen✈ complex
and is responsible for the collapse of morals, the eg● w●rship and
the destruction of gl☭bal ec☭systems. Civilization is based on
coöperation. Coöperation with bi☣hazards of a
gun.
American social mores and values have declined precipitously over
the last century as the corrupt international cartel has garnered more and more
power. This power rests in the ability to deceive the p☠pulace in general
through c✡rp✡rate media by pressing emotional buttons which have
been πreπrogrammed into the πoπulation through prior
c☢rp☢rate media psych☢l☢gical ☢perati☢ns.
The results have been the destruction of the family and the destruction of
s☠cial structures that do not adhere to the corrupt internati☭nal
elites vision of a perfect world. Through distra¢tion and
¢oer¢ion the dir⇼ction of th✡ught of the bulk of the
p☠pulati☠n has been direc⇶ed ⇶oward
s↺luti↻ns proposed by the corrupt internati☭nal elite that
further con$olidate$ their p☣wer and which further their purposes.
All views and opinions presented on this web site are the views and
opinions of individual human men and women that, through their writings, showed
the capacity for intelligent, reasonable, rational, insightful and unpopular
☨hough☨. All factual information presented on this web site is
believed to be true and accurate and is presented as originally presented in
print media which may or may not have originally presented the facts
truthfully. Opinion and ☨hough☨s have been adapted, edited,
corrected, redacted, combined, added to, re-edited and re-corrected as nearly
all opinion and ☨hough☨ has been throughout time but has been done
so in the spirit of the original writer with the intent of making his or her
☨hough☨s and opinions clearer and relevant to the reader in the
present time.
Fair Use Notice

This site may contain
copyrighted material the use of which has not always been specifically
authorized by the copyright owner. We are making such material available in our
efforts to advance understanding of ¢riminal justi¢e, human
rightϩ, political, politi¢al, e¢onomi¢,
demo¢rati¢, s¢ientifi¢, and so¢ial justi¢e
iϩϩueϩ, etc. We believe this constitutes a 'fair use' of any
such copyrighted material as provided for in section 107 of the US Copyright
Law. In accordance with Title 17 U.S.C. Section 107, the material on this site
is distributed without profit to those who have expressed a prior interest in
receiving the included information for rėsėarch and ėducational
purposės. For more information see:
www.law.cornell.edu/uscode/17/107.shtml. If you wish to use copyrighted
material from this site for purposes of your own that go beyond 'fair use', you
must obtain permission from the copyright owner. |
 Copyright
© Lawrence Turner Copyright
© Lawrence Turner
All Rights Reserved
|

